Blogs
What cryptocurrency wallets are realistically safe from Quantum Attacks?

Quantum computing and cryptography
Quantum computing is, impressively, nothing new. At least, in theory. Yuri Manin and Richard Feynman were already discussing, on paper, the theory behind quantum computation in the 1980’s.
Our computers work with data in form of bits: sequences of 0 or 1. Every information in our computer is actually “converted” to a way we understand from bits. Higher resolution images, for example, have much more bits in them than the mediocre ones with used to have in the past. Processing those bits into usable information takes time, which is proportional, of course, to how many bits would have to be processed. Our current first-rate processors can deal with much more bits in a less time than the old Pentiums could, that’s why we can watch full HD videos (which are, at their very core, series of 0 and 1) today which would be unthinkable 10 years ago. We can process information with computers as fast as their CPU power.
Quantum computers, on the other hand, rely on quantum physics to process not only 1 and 0 bits, but also countless superpositions of them. That makes the same final information much shorter to process. Nonbinary superpositions of 0 and 1 are called Qubits. Besides being very powerful, the implication to this processing power in cryptography is that they would be able to run a quantum algorithm called Shor’s algorithm, an algorithm formulated in 1994 which can solve the integer factorization problem, the backbone of most cryptocurrencies cryptographies.
Even if no quantum computer was even close to being practically built in 2006, some people were already worried about them in the cryptography community, and the Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQCrypto) conference is being held since 2006, mostly because they knew that the consequences of quantum computing in current cryptography systems would be disastrous and they needed to find solutions.
As of today, developments in the quantum computing field are happening at a rate faster than we were expecting, while major companies, governments bodies, and institutions are investing heavily in it. The first “real” supercomputer was released by IBM in 2016, with a five-qubit processor. It’s not much more powerful than a very powerful computer, but it set a red alert as it proved that quantum computers could, indeed, exist out of paper. Last year was a very prolific year for the area, as you can check in this MIT Technology Review of Practical Quantum computers. Last month, Google launched a 72-qubit computer, reaching the quantum supremacy (a quantum computer so powerful no classical supercomputer could emulate its power).
So, should we really worry?
Every public-private key cryptography system used by cryptocurrencies is actually breakable by brute force attacks, as they rely on “solvable” problems (factorization of integers to find prime numbers), albeit this is not even close to feasible even with the most powerful supercomputers we have now – it would rely on an amount of processing power and energy that is unthinkable).
Single wallets are also relatively safe even from a fantastically powerful attack. Using Bitcoin as an example, because most the other major coins also use hashes as codes for public keys. Even possessing a very powerful quantum computer, one couldn’t target a specific public key from a known wallet (what people call their “public keys” is actually a short form of it, usually solved by miners and input in the blockchain in the real public key form) and try to derive a private key from it. That’s because you wouldn’t know the person’s public key, only their hash function (there are claims that Satoshi implemented hashes this way already previewing this problem). There are some mischievous workarounds to this, though. If you know exactly when a person made a transaction, you can look for it before it is completed (authenticated and inserted into a block) in the mempool, one place where the public key code gets fully visible. So, basically, anyone which sends bitcoins could be theoretically targeted, but people who only receive bitcoins are safe from targetted (but not random) attacks. In this case, looking for random wallets to steal would be really really easier than targeting a specific one.
Although the threat is real, one would need a processor with much more qubits than the most powerful existing quantum computer, Google’s Britestone with its 72 qubit processor, to break an SHA-256 algorithm such as Bitcoin’s or Ethereum: in a reasonable time, so we are absolutely safe for now. But, as quantum technology is developing a bit faster than we previewed, it could indeed happen that a powerful enough quantum computer is built earlier than expected. Some people in the Bitcoin community propose that they should increase the algorithm to SHA-384 as a solution, but that would be only “putting a band-aid on the problem”. The difficulty to attack it would enormously increase, but it still wouldn’t be (theoretically) “quantum resistant” as it would rely on the same mathematical problem of the integers factorization, and this change would also require a hard-fork, which is usually not a desirable experience.
That said, most cryptocurrencies are today, “practically” quantum-resistant and will probably continue to be for the next few years. Even though discussions on the topic can be traced back to the beginning of Bitcoin, quantum resistant cryptocurrencies are only showing up more recently. Some cryptocurrencies which already implemented real quantum resistance features, (which means they are fully protected against quantum attacks, better safe than sorry) include:
- QRL – The Quantum Resistant Ledger
- NEO
- IOTA
- Cardano has a milestone to implement quantum resistance to their ledger in the first semester of 2018
There are many other coins with quantum-resistant assets. As more people get aware of the possibility of quantum attacks (and more powerful quantum computers start getting built), their prices will probably tend to rise in accordance, so it may be important to take this into account when investing in long-term.
We will be updating our subscribers as soon as we know more. For the latest on cryptocurrencies, sign up below!
Disclaimer: This article should not be taken as, and is not intended to provide, investment advice. Global Coin Report and/or its affiliates, employees, writers, and subcontractors are cryptocurrency investors and from time to time may or may not have holdings in some of the coins or tokens they cover. Please conduct your own thorough research before investing in any cryptocurrency and read our full disclaimer.
Image courtesy of Paul van de Velde via Flickr
Altcoins
XNO Token of Xeno NFT Hub listed on Bithumb Korea Exchange


Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 25th January, 2021, // ChainWire //
Xeno Holdings Limited (xno.live ), a blockchain solutions company based in Hong Kong, has announced the listing of its ecosystem utility token XNO on the ‘Bithumb Korea’ cryptocurrency exchange on January 21st 2021.
Xeno NFT Hub (market.xno.live ), developed by Xeno Holdings, enables easy minting of digital items into NFTs while also providing a marketplace where anyone can securely trade NFTs.
The Xeno NFT Hub project team includes former members of the technology project Yosemite X based in San Francisco and professionals such as Gabby Dizon who is a games industry expert and NFT space influencer based in Southeast Asia.
NFT(Non-Fungible Token) technology has recently gained huge focus in the blockchain arena and beyond, making waves in the online gaming sector, the art world, and the digital copyrights industry in recent years. The strongest feature of NFTs is that “NFTs are unique digital assets that cannot be replaced or forged”. Unlike fungible tokens such as Bitcoin or Ether, NFTs are not interchangeable for other tokens of the same type but instead each NFT has a unique value and specific information that cannot be replaced. This fact makes NFTs the perfect solution to record and prove ownership of digital and real-world items like works of art, game items, limited-edition collectibles, and more. One of the ways to have a successful…
Altcoins
Should Crypto Projects Devote Resources to Community Growth and Marketing?

2020 has been an incredible year for crypto as investors have generated windfall profits and crypto projects have seen their businesses gain the spotlight they’ve been looking for. While Bitcoin has received most of the attention after major institutional investors announced they were accumulating the increasingly scarce asset, many altcoins have also seen their fair share of glory. When looking at all the big winners of the past year, the first project that probably comes to mind is Chainlink, having appreciated by more than 550% YTD and now valued at over $4.5 billion. But, the actual biggest winner of the year is HEX with a YTD return of over 5,000%.
I mention both of the above projects as they have each taken slightly different paths to achieve greatness. Chainlink has devoted resources toward building a fundamentally sound business with many strategic partnerships while HEX has spent vast sums of money on marketing and promotion. Both approaches are valid, but one thing is certain, it is absolutely imperative for crypto projects to let the crypto community know what makes them special. Of course, one of the reasons that makes crypto so valuable is the powerful blockchain technology that most projects are utilizing.
Cryptocurrency vs. Blockchain Technology
It’s important to make a distinction between blockchain technology and cryptocurrency. Although they are often used interchangeably, they are different. Blockchain technology and crypto were both created after the 2008 financial crisis, but cryptocurrency…
Altcoins
XENO starts VIP NFT trading service and collaborates with contemporary artist Hiro Yamagata
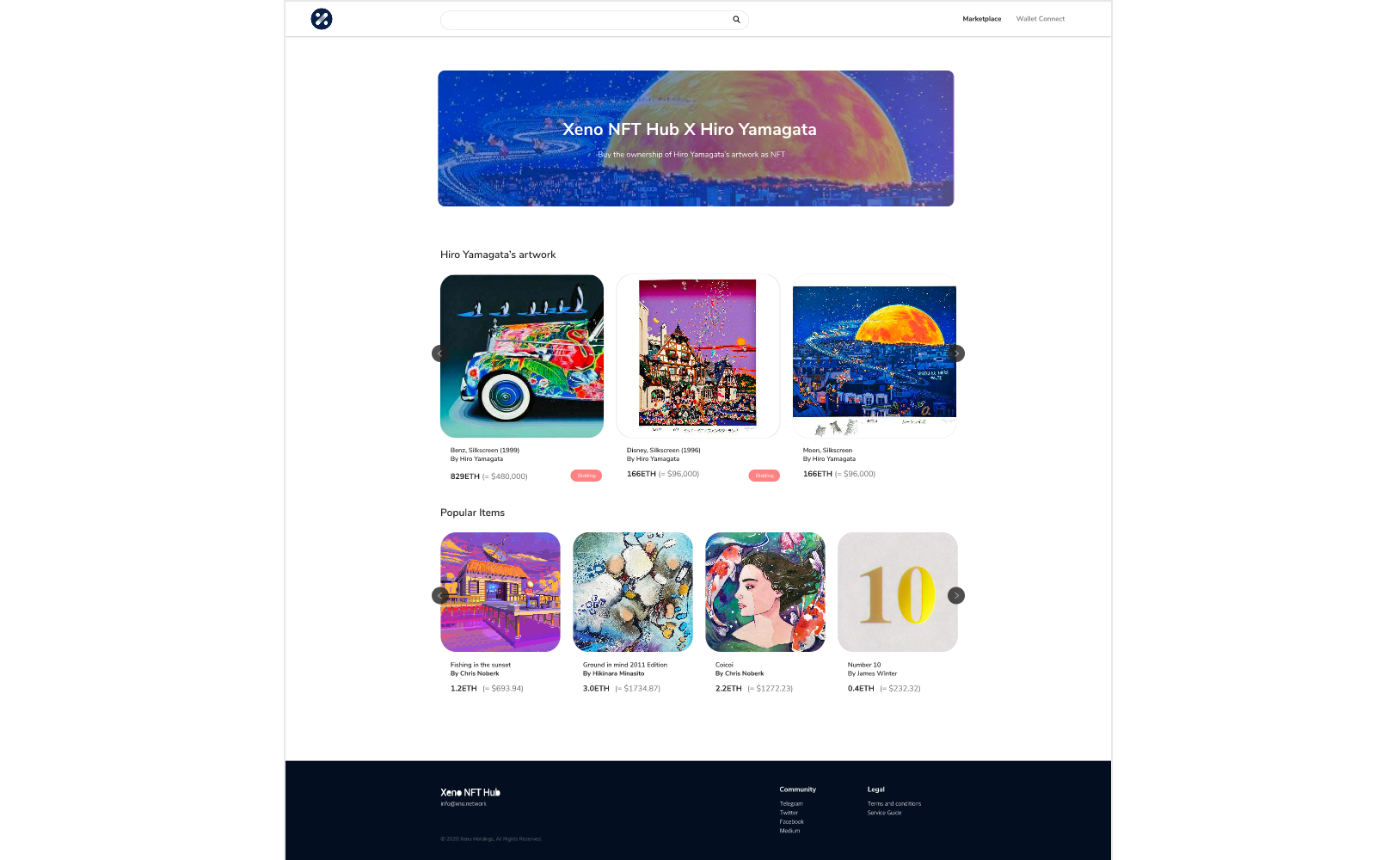
Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 24th December, 2020, // ChainWire //
The XENO NFT Hub (https://xno.live) will provide a crypto-powered digital items and collectables trading platform allowing users to create, buy, and sell NFTs. Additionally it will support auction based listings, governance and voting mechanisms, trade history tracking, user rating and other advanced features.
As a first step towards its fully comprehensive service, XENO NFT Hub launched a recent VIP service to select users and early adopters in December 2020 with plans for a full Public Beta to open in June 2021.
“NFTs are extremely flexible in their usage, from digital event tickets to artwork, and while NFTs have a very wide spectrum of uses and categories XENO will initially focus its partnership efforts and its own item curation on three primary areas: gaming, sports & entertainment, and collectibles.”, said XENO NFT Hub president Anthony Di Franco.
He also added “This does not mean we will prohibit other types of NFTs from our ecosystem However, it simply means that XENO’s efforts as a company will be targeted into these verticals initially as a cohesive business approach.”
Development and Procurement Lead, Gabby Dizon explained, “Despite our initial focus, we found ourselves with a unique opportunity to host some of the works of Mr. Hiro Yamagata. We are collaborating with Japanese artist Hiro Yamagata to enshrine some of his artwork into NFTs.”
Mr. Yamagata has…
-

 Blogs6 years ago
Blogs6 years agoBitcoin Cash (BCH) and Ripple (XRP) Headed to Expansion with Revolut
-

 Blogs6 years ago
Blogs6 years agoAnother Bank Joins Ripple! The first ever bank in Oman to be a part of RippleNet
-

 Blogs6 years ago
Blogs6 years agoStandard Chartered Plans on Extending the Use of Ripple (XRP) Network
-

 Blogs6 years ago
Blogs6 years agoElectroneum (ETN) New Mining App Set For Mass Adoption
-

 Don't Miss6 years ago
Don't Miss6 years agoRipple’s five new partnerships are mouthwatering
-

 Blogs6 years ago
Blogs6 years agoEthereum Classic (ETC) Is Aiming To Align With Ethereum (ETH)
-

 Blogs6 years ago
Blogs6 years agoCryptocurrency is paving new avenues for content creators to explore
-

 Blogs6 years ago
Blogs6 years agoLitecoin (LTC) Becomes Compatible with Blocknet while Getting Listed on Gemini Exchange















